|
|
 Training
Training |
|
|
Training CEED Offered:
|
|
|
|
Although Centre for Environment and Economic Development, CEED offering number of regular trainings related to “Mountain Hazard Management, Disaster Risk Reduction and Management , Climate Change Adoption, Relief and Rehabilitation Management, Need Assessment and Community Based Disaster Management , Water and Sanitation , Search and Rescue”, and now CEED successfully organizing trainings and consultancy in the areas of ; Mountain Agriculture, Watershed Management , Nursery , Floriculture ,Saffron Cultivation and Marketing ,Agro Forestry , Medicinal Plant, Fisheries , Poultry, Dairy ,Seed Management Trainings etc.
|
|
|
Commercial Nursery: |
|
Nurseries can grow plants in open fields, on container fields and in tunnels or greenhouses. In open fields, nurseries grow ornamental trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, especially the plants meant for the wholesale trade or for amenity plantings. On a container field nurseries grow, small trees, shrubs and herbaceous plants, usually destined for sales in garden
Centres. Nurseries also grow plants in greenhouses, a building of glass or in plastic tunnels, designed to protect young plants from harsh weather (especially frost), while allowing access to light and ventilation. Modern greenhouses allow automated control of temperature, ventilation and light and semi-automated watering and feeding. Some also have fold-back roofs to allow "hardening-off" of plants without the need for manual transfer to outdoor beds.
|
|
Most nurseries remain highly labor-intensive. Although some processes have been mechanised and automated, others have not. It remains highly unlikely that all plants treated in the same way at the same time will arrive at the same condition together, so plant care requires observation, judgment and manual dexterity; selection for sale requires comparison and judgment. Business is highly seasonal, concentrated in spring and autumn.
|
|
|
2. Objectives: |
|
The main objectives of this training are to:
|
|
i) |
Train the participants on
modern nursery practices and
problems |
|
ii) |
Hands-on training on Flower cultivation, breeding, irrigation, diseases, cutting, green houses, grafting, fertilizing and seed processing |
|
iii) |
Training on value addition and quality control for better economic gain from the products by the nursery activities. |
|
|
|
|
3. Target Participants: |
|
• |
This training programme is targeted for technical/professional staff/processors/ farmers. |
|
|
4. Expected outcomes: |
| The participants will acquire knowledge and skills on advanced floriculture and nursery practices related to processing/ preservation, packaging and marketing of flower bearing plants. The participants will also be exposed to latest developments in technology and hands-on training at different nurseries/processing plants. |
|
|
Floriculture: |
|
|
|
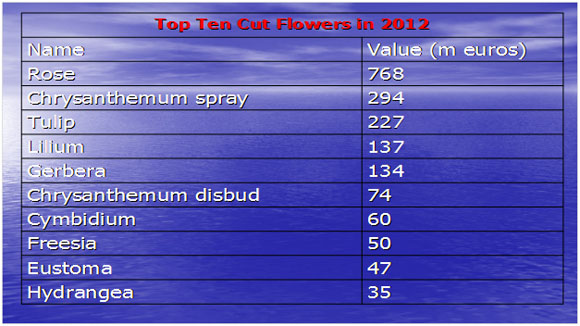
Floriculture or flower farming, as it is popularly called, is a discipline of Horticulture, and is the study of growing and marketing of flowers and foliage plants. Floriculture includes cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants for sale or for use as raw materials in cosmetic and perfume industry and in the pharmaceutical sector. The floral industry today has grown to a much larger proportion and offers a wide scope for growth and profits. Floriculture is fast emerging venture on the world scenario growing at a modest annual rate of about 8-10 percent. This has become a potential money-spinner activity for the third world countries. Total value of flowers and floricultural products at wholesale level has been recorded over 50 billion US$ from about 2 million hectare area. Total value of all floricultural products from 191 countries has crossed over 20.8 billion US$ in 2011 (www.uncomtrade.com).
|
 |
|
|
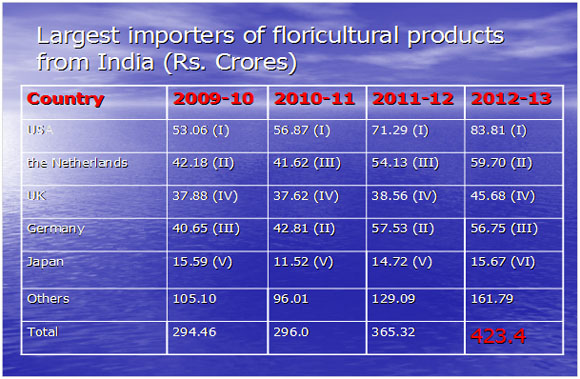
In India, floriculture is also being viewed as high growth activity in agriculture sector. The area under flower crops has increased from thirty thousand hectares in 1993 to 2.53 lakh hectares in 2012 (www.nhb.gov.in). Indian floriculture industry is fast becoming more aware of the importance of offering products according to the wishes of consumers. With the changing trends and a constant urge for new innovative products in domestic and foreign flower markets, therefore, the flower growers have to respond immediately. The export of total floricultural products has increased from Rs. 14.5 crores in 1991-92 to over 423.4 crores in 2013 (www.apeda.com).
|
 |
|
|
The nature has endowed Himachal Pradesh with a variety of agro-climatic conditions due to which large number of flower crops with excellent quality can be produced throughout the year in one or the other part of the state. The climate in the state ranges from sub-tropical to wet and dry temperate. Flower cultivation has eminent role in amelioration of the hill environment and to boost the rural economy of the state, which owes because of the following points viz., generating various sources of cash income to the hill and mountain people, generating employment opportunities in pre and post harvest activities in this sector, satisfying aesthetic needs of the people and developing sustainable agriculture system in hill and mountain areas.
|
|
|
In India, Floriculture industry comprises flower trade, production of nursery plants and potted plants, seed and bulb production, micro-propagation and extraction of essential oils. Though the annual domestic demand for the flowers is growing at a rate of over 25% and international demand at around Rs 90,000 crore, India's share in international market of flowers is negligible. India has a blooming future as far as floriculture is concerned. Enormous genetic diversity, varied agro-climatic conditions, versatile human resources etc, offer India a unique scope for judicious employment of existing resources and exploration of avenues yet untouched.
|
|
|
The employment opportunities in this field are as varied as the nature of work itself. One can join the field of floriculture as farm/estate managers, plantation experts and supervisors, project coordinators etc. Research and teaching are some other avenues of employment in the field. Marketing of floriculture products for different ventures is emerging as a potential segment of this field. Besides, one can work as a consultant, landscape architect etc with proper training. One can also work as entrepreneur and offer employment to others. In addition to these careers, which involve research and actual growing of crops, floriculture also provides service career opportunities, which include such jobs as floral designers, groundskeepers, landscape designers, architects and horticultural therapists. Such jobs require practitioners to deal directly with clients. |
|
|
Advance SEED processing and Value Addition: |
|
|
|
Good and healthy Seeds always-prominent ingredients to nourish the plant and food production process. Quality Seed can be harvested from the better-managed crop yields. Seed harvesting, conservation and managements improve livelihoods for all sections of the rural community based upon economically viable activities – food production, off-farm employment and trade - social cohesion and sustainable use of natural resources. This training will bring together stakeholders including SMEs, technical officials, business groups, farmers, etc., to exchange views and ideas pertaining to variety choice, seed multiplication, exchange and marketing. The fairs attract a wide range of stakeholders including seed enterprises, farmers, NGOs, seed and agro-chemical dealers, research institutes, donors, senior MRRD /MAIL officials and many other stakeholders. |
|
Quality seed is one of the most important input factors governing the yield potential of a crop. Use of unhealthy insect and disease attacked seed will just bring the disaster to farmers. Therefore, it is imperative to supply farmers quality seed of various crops. Freshly harvested and threshed seed is generally fit for growing a new crop. But it has to be stored for some period ranging from a few days to numerous years because of unfavourable climatic conditions or dormancy for germination or for national reserve. The raw seed though genetically pure, contains a lot of undesirable material like weed seeds, seeds of other crops or varieties or damaged seed. Therefore it has to be processed and upgraded for better and uniform crop stand in the next crop season. The main cause for damage of seed is the moisture content. N The deterioration in seed quality is initiated at moisture content above 15% due to mould growth, heating due to increased respiration and activities of micro-organisms. To avoid such losses in seed quality and to maintain it, the seed has to be artificially dried to 10-12% moisture content before storing. The seed has to be dried as soon as it is harvested.
|
|
Seed lots usually contain inert material, weed seeds, deteriorated and damaged seeds, off-size seeds etc. Seed cleaning and upgrading to remove or reduce to the extent possible, the various undesirable material and to get a uniform size seed so as to upgrade its overall quality is a must. The cleaning process is done on the basis of differences in physical properties of desirable seed and undesirable matter i.e. seed size, density, shape, surface texture, colour etc. Most often, satisfactory processing requires that lots be processed in a specific sequence through several operations.Seed is covered with some organic compounds to protect it from storage loss or loss to the germinating young seedlings by organisms like fungi, bacteria and viruses in the soil. The seed treatment is generally done with materials in the form of dust, wettable powders or liquids.
|
|
Packaging material must provide protection against high relative humidity. Under dry warehouses and storage conditions, the use of cotton, jute and paper bags is the most satisfactory method of seed packaging. While in high humidity locations, some moisture proof containers like aluminium-polythene laminated pouches, polythene bags of over 700 gauge thickness, sealed tins etc. are good for this purpose.A reliable seed test, conducted by seed testing laboratories, will avoid the use of inferior seed and is mandatory. Seed testing is done for judging the physical purity, germination and moisture content as per the minimum seed standards. Seed of the new crop varieties, superior in some quantitative and qualitative characteristics to existing ones, should be made available in appreciable quantity to farmers in areas for which the varieties are most suitable. The farmers who purchase seed should be sure of buying good seed of specific varieties. To provide a reasonable guarantee of the genetic quality of seed prior to sowing, seed quality control systems work in India with the aim of thorough supervision of the entire seed production system. This involves keeping records of the multiplication of varieties and inspection of the seed production field, seed processing, seed treatment, testing and finally packaging for marketing. Each bag, package or container is labelled to prove that it is part of a certified lot. Labelling the bags is the concrete act of certification and provides the tangible document of certification to each buyer.
|
|
|
4. Expected outcomes: |
|
|
|
The participants will acquire knowledge and skills on various aspects of quality seed production, maintenance of seed purity, processing and packaging of seed. The participants also exposed to latest developments in technology and hands-on training at different seed quality control, management and marketing strategy.
|
|
|
Saffron Cultivation and Value Addition: |
|
|
|
Saffron is the most expensive spice of the world, which grows in only two or three places in the entire world. The use of the spices dates back to 1500 B.C. in some parts of the world like Spain, Europe and in Greece but in Asia Minor it was cultivated from the last 100 years used in Perfumes, dyes,food and beverage flavoring. Today Spain has emerged to be world’s largest producer of the valuable Spice. Other places like Iran, France, Italy, Afghanistan and some pockets of India like in the Kinor valley of Himachal Pradesh and Kashmir valleys in Jammu and Kashmir.There are different types of Saffron: Lachha Saffron, Mogra Saffron, Patti Saffron, and Chora Saffron. It is used for coloring and flavoring confectionary items. It also exhibits certain medicinal properties. Saffron is known to be infested with fungal and viral diseases, which are carried over by corms and thereby affect corm yield. Saffron the, the spice is obtained from trifid stigma and hence yield depends upon flowering alone. There is need to follow standardized protocols for mass cultivation by quality planting material. The Dry Fruits contain all the necessary nutrients required for the body, hence all these nutrients are to be preserved while packaging and supplying them to maintain the quality. For that matter post harvest, processing is required to remove the water content from the products to prevent damage and increase the shelf life of the products. Value addition of the produce is also practiced to get more profit from the produces in comparison to normal processing.
|
|
The crop holds is significance as the most expensive crop grown in the mountain areas which has a huge demand in the market and the supply being significantly low. The crop can help combat the mountain poverty and provide gainful employment. The Saffron production today is going down due to the fungal diseases that mainly infect the corm (corm rot) of the Saffron plant. Thus it becomes important to study how to free the plant from diseases and it becomes important to learn and exchange ideas of different mountain communities who cultivate Saffron about the methods of cropping for a maximum yield. Thus with this intention this program is scheduled for the trainees of Afghanistan. It intends to make them understand and analyze the method of cultivation of the spice in India and share their knowledge about the cultivation in Afghanistan
|
|
|
2. Objectives: |
|
|
|
The main objective of this training is to |
|
i. |
Train the participants on standardized protocols of mass cultivation by quality planting material. |
|
ii. |
On hand training on scientific preservation/processing, packaging and marketing to maintain quality, prevent damage and increase shelf life |
|
iii. |
Training on value addition |
|
iv. |
Knowledge exchange and networking among the saffron Entrepreneur |
|
|
3. Target Participants: |
|
|
|
This training programme is targeted for technical/professional staff/processors/ farmers. |
|
|
4. Expected outcomes: |
|
|
|
The participants will acquire knowledge
and skills on advance cultivation,
processing / preservation, packaging and
marketing. The participants will also be
exposed to latest developments in
technology and on hand training at
different processing plants
|
|
|
Poultry Farm Management and Marketing: |
|
|
|
Poultry Farming have been one of the most important subsidiary occupation of the farming community in many countries. Poultry Farming is a remunerative business both in rural and urban areas due to the requirement of small space, low capital investment and quick return throughout the year. It has a significant role in the eradication of malnutrition and poverty as well as eliminating un- and under-employment among the rural masses. However, due to lack of modern and updated method of farming, farmers are practicing their own way which has been found to be unproductive and not commercially viable.
|
|
Poultry farming is a profitable business. It provides an excellent opportunity for self-employment of unemployed youth. It is important source of income generation to small/marginal farmers and agricultural labourers working with poultry farming. Poultry farm managers are responsible for the day-to-day running of the farm, which includes monitoring the welfare of the birds, feeding them and ensuring fresh drinking water is always available. They may also be managing staff in order to compile work rotas, pay and holiday entitlements. Managers are also responsible for maintaining the site, ensuring it is kept clean and tidy at all times and that it complies with the relevant health and safety regulations. The health of the flock is most important, and managers need to be vigilant and able to act on any health issues that may occur. This type of work is carried out in all weathers, both indoors and outdoors, and can involve long and unsociable hours. Managers will often need to be available for shifts that include weekends and bank holidays. The work can be seasonal, particularly with turkey flocks. The housing of indoor flocks can be dark, smelly and very dusty. Managers will need business skills as well as poultry experience. The increased demand of eggs and other products in the national/ international market has created immense scope for poultry farming as an alternative to traditional agriculture.
|
|
|
2. Objectives: |
|
|
|
The main objective of this training is to |
|
iv) |
Train the participants on modern
poultry farming practices and
problems faced by the farm
managers. |
|
v) |
Hands-on training on
scientific processing/
preservation, packaging and
marketing to maintain
quality and increase shelf
life of the products. |
|
vi) |
Training
on value addition and
quality control for better
economic gain from the
produces by the farming
activities. |
|
|
3. Target Participants: |
|
|
|
• |
This training programme is
targeted for
technical/professional
staff/processors/ farmers. |
|
|
4. Expected outcomes: |
|
|
|
The participants will acquire knowledge and skills on advanced poultry farming, processing/ preservation, packaging and marketing. The participants will also be exposed to latest developments in technology and hands-on training at different farms/processing plants.
|
|
|
Dairy Farming and Product Marketing |
|
|
|
1. Background: |
|
|
|
Dairy farming is a
profitable business. It
provides an excellent
opportunity for
self-employment of
unemployed youth. It is not
only an important source of
income generation to
small/marginal farmers and
agricultural laborers but
also provide quality protein
to the human population of a
country. Since agriculture
is mostly seasonal, there is
a possibility of finding
employment throughout the
year for many persons
through dairy farming. In
addition to this, the
surplus fodder and
agricultural by-products are
gainfully utilized for
feeding the animals.
Bullocks are used for
draught power for farm
operations and
transportation. The manure
from animals provides a good
source of organic matter for
improving soil fertility and
crop yields. The gober gas
from the dung is used as
fuel for domestic purposes
as also for running engines
for drawing water from well.
Dairy farming can also be
taken up as a main
occupation around big urban
Centres where the demand for
milk is high. |
|
The increased demand of milk & milk products in the national/ international market has created immense scope for dairy farming as an alternative to traditional agriculture.
|
|
|
2. Objectives: |
|
|
|
The main objective of
this training is to |
|
i. |
Train the participants on modern
dairy farming practices and
problems faced by the farmers. |
|
ii. |
On hand training on
scientific processing/
preservation, packaging and
marketing to maintain
quality and increase shelf
life of the produces. |
|
iii. |
Training on value addition
and quality control for
better economic gain from
the produces by the farmers. |
|
|
3. Target Participants: |
|
|
|
This training programme is targeted for technical/professional staff/processors/ farmers. |
|
|
4. Expected outcomes: |
|
|
|
The participants will acquire knowledge and skills on advanced poultry farming, processing/ preservation, packaging and marketing. The participants will also be exposed to latest developments in technology and hands-on training at different farms/processing plants.
|
|
|
Food processing |
|
|
|
India is the world's second largest producer of food next to China, and has the potential of being the biggest in the food and agricultural sector. The total food production in India is likely to double in the next ten years and there is an opportunity for large investments in food and food processing technologies, skills and equipment, especially in areas of Canning, Dairy and Food Processing, Specialty Processing, Packaging, Frozen Food/Refrigeration and Thermo Processing. Fruits & Vegetables, Fisheries, Milk & Milk Products, Meat & Poultry, Packaged/Convenience Foods, Alcoholic Beverages & Soft Drinks and Grains are important sub-sectors of the food processing industry. Health food and health food supplements are another rapidly rising segment of this industry, which is gaining vast popularity amongst the health conscious. |
|
India's food processing sector covers fruit and vegetables, meat and poultry, milk and milk products, alcoholic beverages, fisheries, plantation, grain processing and other consumer product groups like, confectionery, chocolates and cocoa products, soya-based products, mineral water, high protein foods etc. The most promising sub-sectors are Soft drink bottling, Confectionery manufacture, Fishing, Aquaculture, Grain-milling and grain-based products, Meat and poultry processing, Alcoholic beverages, Milk processing, Tomato paste, Fast food, Ready-to-eat breakfast cereals, Food additives, flavors etc.
|
|
|
Medicinal plants |
|
|
|
It is a recognised fact that
India presents a great
investment and business
opportunity in the herbal
sector, with the prospects
of the country emerging as a
global leader in the field.
It is also well known that
Tamilnadu is a significant
player in the herbal
industry, with substantial
production and market share. |
|
In recent times, there has
been an enlightened
awareness among the citizens
of the country about the
natural advantages that this
country is endowed with.
This is particularly
conspicuous in the area of
the indigenous therapy or
alternative medicine. A
general view that such
medicines could be taken
recourse to, for better and
safe therapeutic effect, has
definitely been established.
Main reasons for a shift
“Back to Natural” is
peoples' concern over
toxicity and side effects of
modern drugs, realisation
that natural medicines are
safer, allopathic drugs are
often ineffective against
many chronic complaints, the
medical fraternity has begun
to acknowledge the value of
some herbal medicines.
Further, herbal medicines
are generally less expensive
than allopathic drugs. |
|
|
Vermicompost |
|
|
|
Vermicompost is an organic
manure (bio-fertiliser)
produced as the vermicast by
earthworm feeding on
biological waste material,
plant residues etc. This
compost is an odourless,
clean, organic material
containing adequate
quantities of N P K and
several micronutrients
essential for plant growth.
Vermicompost is a preferred
nutrient source for organic
farming. It is eco-friendly,
non-toxic, consumes low
energy input for composting
and is a recycled biological
product. |
|
The organic wastes that are available in agricultural areas include cattle-dung, sheep-dropping, biogas slurry, stubble from harvested crops, husks and corn shells, weeds, kitchen waste etc. All these materials can be used to produce vermicompost.
|
|
|
Agro-forestry |
|
|
|
Ever since man began
cultivating crops and
domesticating animals, he
has been practicing
agro-forestry as these
activities took place along
forest areas. Agro-forestry
is the system of land use
that combines growing and
raising of crops and/or
livestock along with plants
that belong to the forest.
The land can be used to
raise agricultural crops and
trees and to rear animals.
Some examples are shifting
cultivation, growing of tea
and coffee under the shade
of trees, inter-cropping
under coconut trees, and
home gardens. In fact, most
farmers in India grow
agricultural crops, rear
animals, and plant certain
trees on their land, often
on the boundary area.
Agro-forestry reduces the
farmers’ dependency on
forests even as it provides
them economic benefits. It
results in more diverse,
healthy, and sustainable
land-use systems. It focuses
on meeting the economic,
environmental, and domestic
needs of people on their
private lands. For hundreds
of years, farmers have
nurtured trees in their
fields, pasturelands, and
around their homes. |
|
Agro-forestry is defined by
some as a dynamic,
ecologically - based natural
farm management system that,
along with agriculture and
the integration of trees on
farms, has many
environmental benefits. Put
simply, agro-forestry is
using trees on farms. Trees
can provide many products
such as timber, fodder, fuel
wood, medicines, and oils.
It also helps to conserve
soil, enhance soil
fertility, and provide
shelterbelts for crops and
fruit trees.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Top |
|
|